SQL Server user makes the frequent use of stored procedures in the database in order to maintain the integrity and consistency of the data. Simply, a block of SQL query is embedded into the stored procedure, which can be called at any time in the program. Since, these procedures are associated in the encrypted form with the database application, one finds it quite difficult to view the code behind a particular stored procedure. Only the permitted users are allowed to view the source code behind the stored procedure. More importantly, the developers who wish to update the already included stored procedures in an application, finds it much necessary to decrypt encrypted SQL server stored procedure so that they can easily work on the code and may update the behavior of the procedure. Keeping in mind the need of decryption, we have attempted to provides way to decrypt SQL Server stored procedure using different methods.
Manual Approach to Decrypt SQL Server Stored Procedure
Any stored procedure can be decrypted by using the DAC(Dedicated Administrator Connection) with SQL Server.
To connect to DAC: The DAC can be connected to SQL Server Management Studio by prefixing ADMIN to the server name in query editor.
Once a connection is established with DAC, the decryption can be performed using the following steps:
- Using DAC connection, fetch the encrypted values of the stored procedure
- Obtain the encrypted value for the blank procedure having ‘-’ character in its definition
- Obtain the plain text blank procedure statement in unencrypted form
- Now, XOR the results of step 2 and step 3 to get the final decrypted value of the procedure
Consider the following script that allows to decrypt encrypted stored procedure named ‘dbo.MyDecryption’ using DAC. The scripts needs to be executed carefully, otherwise if any of the parameter is missing, it will generate an error.
SET NOCOUNT ON
GO
ALTER PROCEDURE dbo.MyDecryption WITH ENCRYPTION AS
BEGIN
PRINT 'This is the decrypted text preview..'
END
GO
DECLARE @encrypted NVARCHAR(MAX)
SET @encrypted =(
SELECT imageval
FROM sys.sysobjvalues
WHERE OBJECT_NAME(objid) = 'MyDecryption’)
DECLARE @encryptedLength INT
SET @encryptedLength = DATALENGTH(@encrypted) / 2
DECLARE @procedureHeader NVARCHAR(MAX)
SET @procedureHeader = N'ALTER PROCEDURE dbo.MyDecryption WITH ENCRYPTION AS '
SET @procedureHeader = @procedureHeader + REPLICATE(N'-',(@encryptedLength - LEN(@procedureHeader)))
EXEC sp_executesql @procedureHeader
DECLARE @blankEncrypted NVARCHAR(MAX)
SET @blankEncrypted = (
SELECT imageval
FROM sys.sysobjvalues
WHERE OBJECT_NAME(objid) = 'MyDecryption’)
SET @procedureHeader = N'CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.MysDecryption WITH ENCRYPTION AS '
SET @procedureHeader = @procedureHeader + REPLICATE(N'-',(@encryptedLength - LEN(@procedureHeader)))
DECLARE @cnt SMALLINT
DECLARE @decryptedChar NCHAR(1)
DECLARE @decryptedMessage NVARCHAR(MAX)
SET @decryptedMessage = ''
SET @cnt = 1
WHILE @cnt <> @encryptedLength
BEGIN
SET @decryptedChar =
NCHAR(
UNICODE(SUBSTRING(
@encrypted, @cnt, 1)) ^
UNICODE(SUBSTRING(
@procedureHeader, @cnt, 1)) ^
UNICODE(SUBSTRING(
@blankEncrypted, @cnt, 1))
)
SET @decryptedMessage = @decryptedMessage + @decryptedChar
SET @cnt = @cnt + 1
END
SELECT @decryptedMessage
Decrypt Encrypted SQL Server Stored Procedure using Third Party Tool
Various third party tools for decrypting SQL Server database objects are available in the industry, which cater the demand to easily decrypt the encrypted database objects. One such efficient tool is SQL Decryptor. The tool carries out decryption in the following easy steps:
- Enter all database credentials such as server name, login mode, user credentials(name & password) to connect to server
- On the preview page, choose the required stored procedure and preview the decrypted script in the text box.
- Under the export options, choose to export the decrypted file to SQL Server directly or export as SQL Compatible Script.
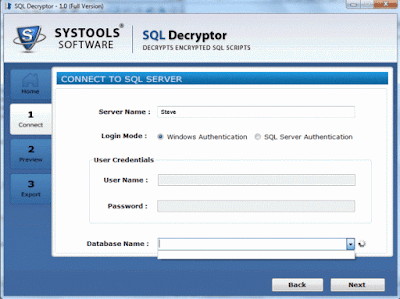
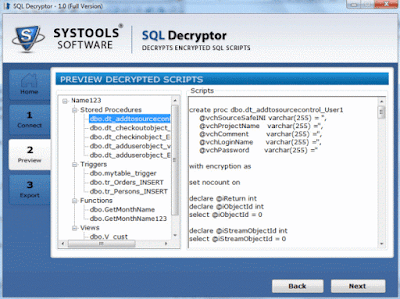
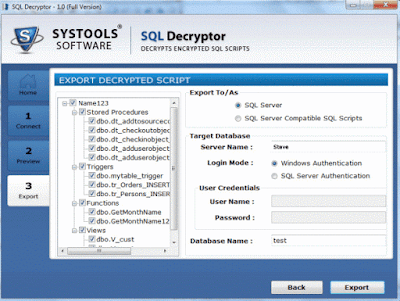
So, the users can make the use of automated decryption tool to decrypt the stored procedures without running any complicated queries.
Conclusion
Considering user’s requirement to decrypt various database objects like the stored procedures, we have tried to explain the method to decrypt encrypted SQL Server stored procedure using manual methods and third party software. Users are advised to run the SQL script carefully to completely decrypt the stored procedure. However, to get rid of the complicated queries the user can also go for the third party SQL Decryptor software. It can efficiently decrypt the database objects and the decrypted script can also be exported using the tool.